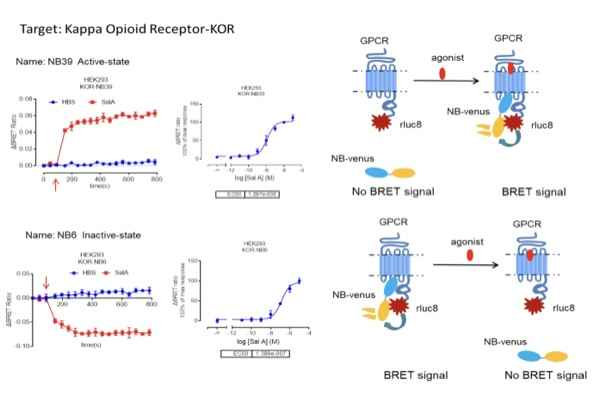
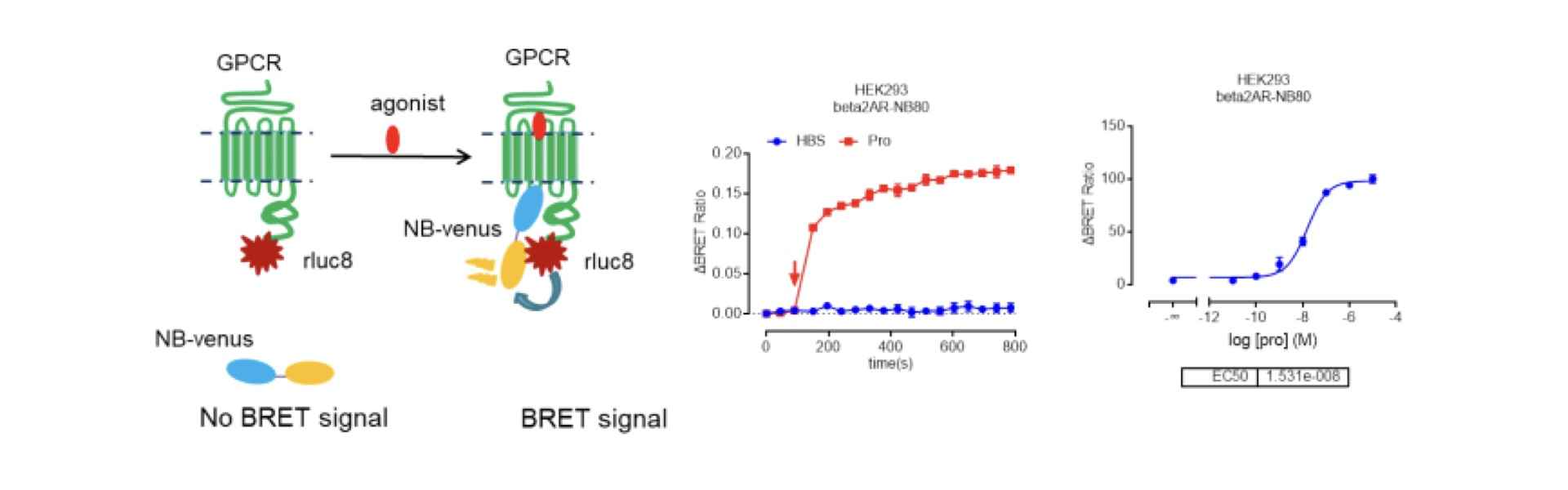
According to relevant reports, NB80 can recognize the activation state of β2AR. By constructing a functional plasmid for the BRET assay and conducting tests, it was observed that NB80 can effectively detect the activity status of β2AR. This suggests that nanobodies capable of specifically recognizing GPCR activation/non-activation states under normal conditions can be designed into BRET assays for real-time monitoring of receptor activity. Additionally, due to the nanobody's specificity for this receptor, it remains unaffected by the activity of other receptors, providing a unique advantage in functional tests such as receptor heterodimerization.
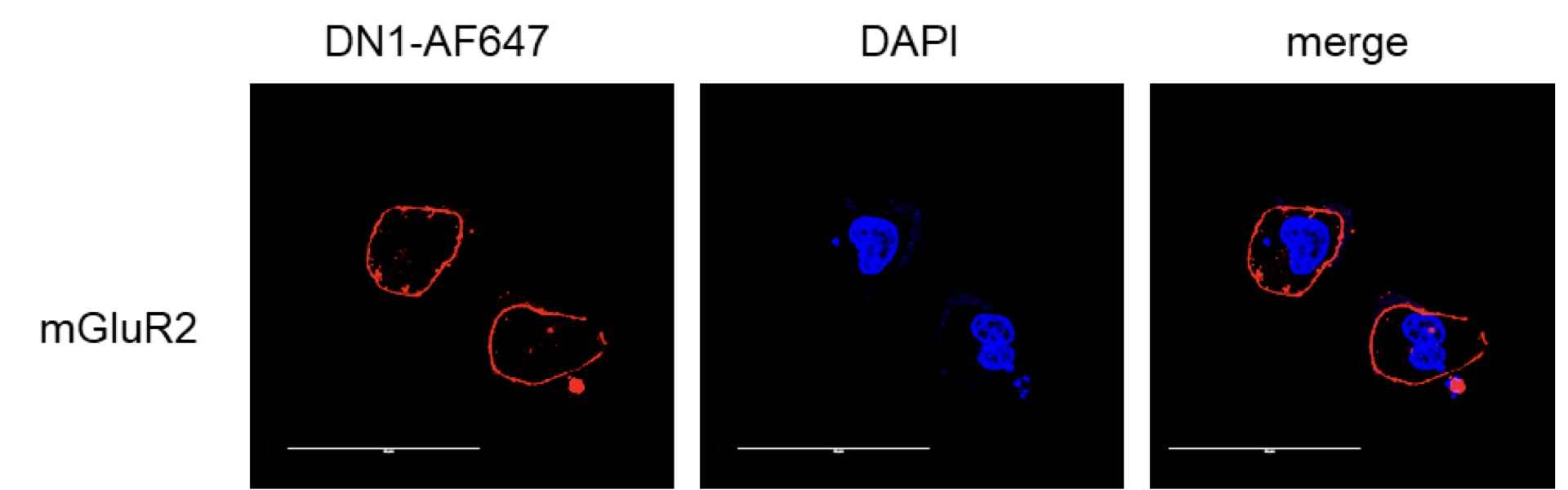
Nanobodies can also be labeled with fluorescent molecules such as AF488/AF647 for cellular imaging. For instance, the mGluR2 nanobody DN1 labeled with AF647 can be utilized for cellular imaging:
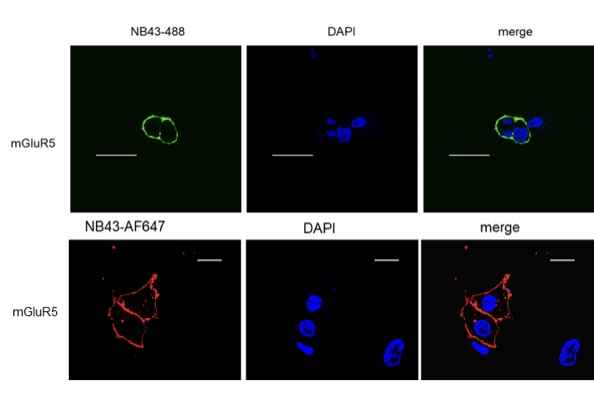
mGluR5 nanobody NB43 labeled with AF488 or AF647 provides flexibility for various experimental requirements:
To address issues like steric hindrance caused by larger labeling molecules affecting antibody affinity, an FC fragment can be added to the nanobody. FC modification allows customization with human-FC, mouse-FC, rabbit-FC, etc., based on experimental requirements, providing versatility for different experiments.
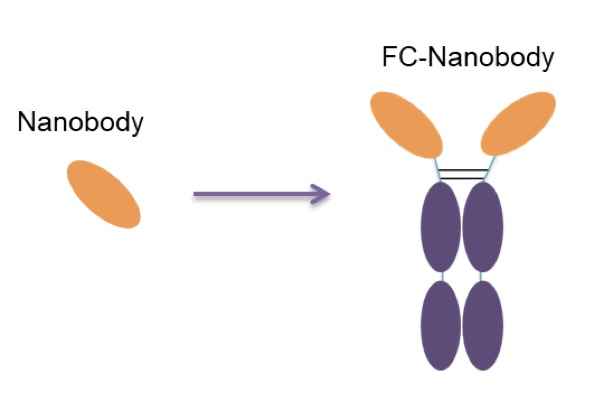
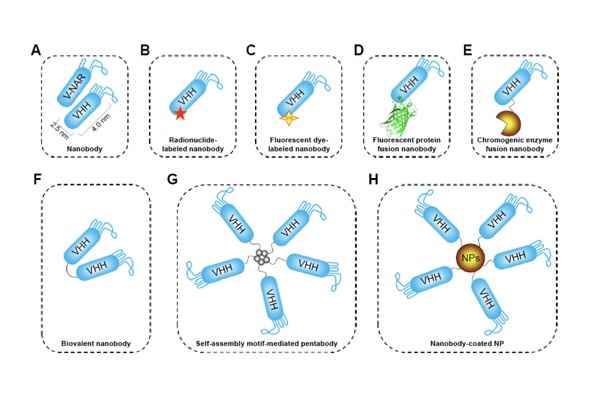
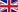
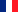
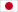
In summary, nanobodies can be labeled and modified through methods such as fluorescent molecule labeling, fusion with fluorescent proteins, fusion with enzyme molecules, and linking multiple nanobody monomers in tandem. These approaches enable nanobodies to exhibit a variety of functions, catering to diverse experimental requirements.