Clinical Applications of PD-1 Antibodies
The immunosuppressive function of PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1 makes this pathway a key factor in tumor immune escape. By blocking the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1, PD-1 antibody drugs can reverse the suppressed state of T cells, activate their attack on tumor cells, and restore the immune system's ability to recognize and eliminate tumors. Currently, PD-1 antibodies are at the forefront of cancer immunotherapy, widely used in treating various cancers including non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, head and neck cancer, and renal cell carcinoma. In these treatments, PD-1 antibodies such as Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab have significantly improved patients' overall survival and progression-free survival.
However, the inhibitory function of PD-1 is not only related to tumor immune escape but also plays a crucial role in various autoimmune diseases. In these conditions, the functional inhibition mediated by PD-1 helps prevent the immune system from attacking self-tissues. For instance, in diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes, the role of PD-1 may help reduce excessive immune responses and attacks on self-antigens. Therefore, PD-1 antibodies are not only vital in cancer immunotherapy but also show potential in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
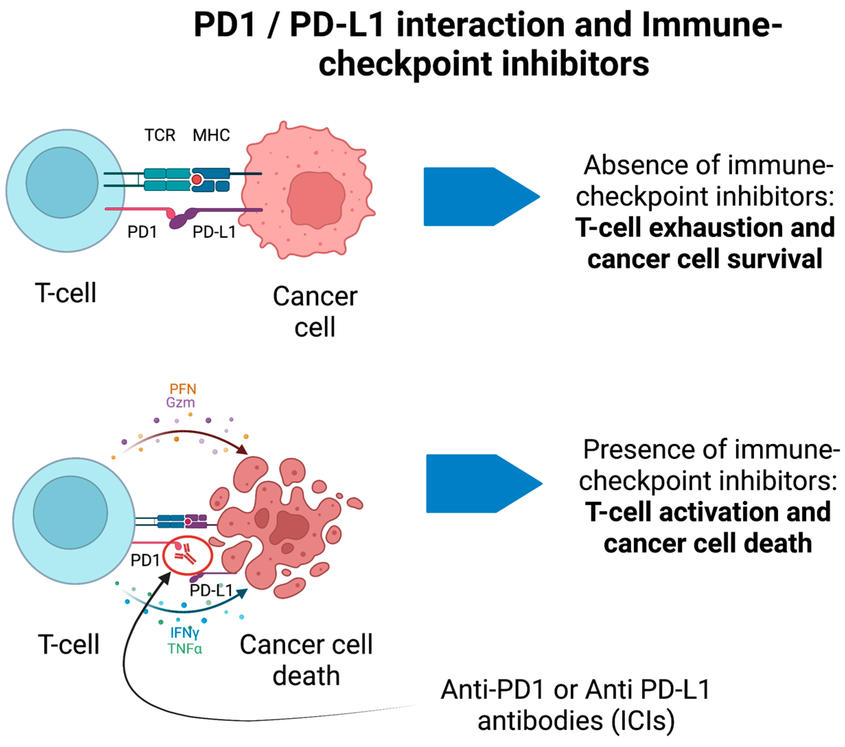
PD1 / PD-L1 interaction and Immune checkpoint inhibitors [1]
PD-1 Antibody Drugs and Clinical Treatment Cases
In recent years, significant progress has been made in the field of PD-1 antibody drugs for cancer immunotherapy, particularly in clinical applications and drug development, with new antibody drugs continuously emerging and treatment areas gradually expanding. Besides PD-1 inhibitors, the application of PD-1 agonists in autoimmune diseases is also becoming a new research direction. The following details the drug information, pharmacological mechanisms, and antibody formats of PD-1 inhibitors and agonists.
1. PD-1 Inhibitors: Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab
Nivolumab (trade name Opdivo) and Pembrolizumab (trade name Keytruda) are the most renowned PD-1 inhibitors, having demonstrated significant efficacy in multiple cancer types. They work by blocking the binding of the PD-1 receptor to PD-L1, relieving immune suppression, restoring T cell attack capability, and thereby enhancing the clearance of tumor cells.
The antibody format for both drugs is IgG4. Their mechanisms are similar, primarily involving the release of immune checkpoint inhibition and activation of T cell immune responses to achieve anti-tumor effects. These drugs have been approved for treating various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, head and neck cancer, and renal cell carcinoma.
2. Atezolizumab and Durvalumab
Atezolizumab (trade name Tecentriq) and Durvalumab (trade name Imfinzi) are antibodies targeting PD-L1, primarily used to block the interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1. Atezolizumab has an IgG1 antibody format and can enhance immune responses through Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC). Durvalumab is also an IgG1 class antibody with a similar immune mechanism. Both have shown significant efficacy in treating non-small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, and urothelial carcinoma.
These drugs not only play an important role in countering tumor immune escape but also improve efficacy in combination therapies, especially when PD-1 inhibitors are combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors, significantly enhancing treatment outcomes and patient survival rates.
3. Latest PD-1 Inhibitors and Clinical Research
In recent years, besides the aforementioned PD-1 inhibitors, many new PD-1 inhibitors are undergoing clinical trials. For example, novel PD-1 inhibitors like ENV-101 and GSK3050002 are under clinical investigation and have shown preliminary success in treating different tumor types. Clinical data indicate that these new drugs offer significant advantages in enhancing T cell-mediated anti-tumor immune responses and reducing side effects.
Combination therapy with PD-1 inhibitors has become a new trend, particularly the combination of PD-1 antibodies with other immunotherapeutics or chemotherapeutic agents. For instance, the combination of Nivolumab + Ipilimumab (a CTLA-4 inhibitor) has demonstrated higher response rates in melanoma and lung cancer patients and can overcome resistance seen with single-agent therapy.
4. Application of PD-1 Agonists in Autoimmune Diseases
Unlike PD-1 inhibitors, which are primarily used in cancer treatment, PD-1 agonists are mainly intended for autoimmune diseases. The activation of PD-1 is typically an important mechanism for immune tolerance. Excessive inhibition of the PD-1 pathway can lead to an overactive immune system, potentially triggering or exacerbating autoimmune diseases. Therefore, appropriate agonism of PD-1 may help restore immune system balance, mitigate excessive immune responses, and alleviate symptoms of autoimmune diseases.
In recent years, research on PD-1 agonists has gained increasing attention, particularly for their potential in treating autoimmune diseases such as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), and Type 1 Diabetes. PD-1 agonists like ABBV-181 and BMS-936559 are being evaluated in clinical trials for their efficacy in autoimmune diseases.
ABBV-181 is a fully human PD-1 agonist antibody initially designed for cancer treatment. However, clinical trials have also found that it can effectively modulate immune tolerance and reduce excessive immune reactions in patients with autoimmune diseases. It acts by agonizing the PD-1 receptor, promoting the expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs), thereby enhancing immune tolerance and suppressing autoimmune responses.
Additionally, BMS-936559, as a PD-1 agonist, has also garnered attention in clinical research for autoimmune diseases. Preliminary studies suggest that BMS-936559 can enhance immune tolerance, alleviate pathological symptoms in autoimmune diseases like SLE, and holds potential therapeutic value.
Advantages of Nanobodies in PD-1 Antibody Drug Development
Nanobodies, as small single-domain antibody proteins, possess many advantages not found in traditional antibodies, showing very broad application prospects especially in tumor immunotherapy and the treatment of autoimmune diseases. In the development of PD-1 antibody drugs, nanobodies offer several unique advantages. Firstly, due to their smaller molecular weight, nanobodies can more easily penetrate cells and tissues, rapidly entering the tumor microenvironment or areas requiring immune tolerance, thereby enhancing therapeutic effects. Furthermore, the structure of nanobodies is more stable, allowing for a longer half-life in vivo, reducing clearance by the immune system, and improving the drug's bioavailability.
In the development of PD-1 antibodies, the application of nanobodies can significantly enhance drug targeting and efficacy. Because nanobodies have a single-domain structure, they can be engineered with higher precision for modifications, improving stability, solubility, and selectivity. For example, PD-1-specific nanobodies can not only bind to and block the PD-1 receptor more efficiently but also exert better immune activation effects within the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, due to their unique small molecular properties, nanobodies can reduce side effects associated with traditional antibody therapies, such as immunotoxicity or allergic reactions.
NBLST possesses the pDual phage display technology, which builds upon the efficient development of traditional phage display by seamlessly integrating mammalian cell production, greatly improving the efficiency of screening out problematic molecules. The NabLib® mammalian cell display technology not only enhances the developability of screened molecules but also allows flexible selection of antibody screening formats, providing better support for downstream applications and detection of antibody molecules.
Simultaneously, NBLST launches the PD-1 Off-the-Shelf Immune Library. After completing alpaca immunization, we collect whole blood and isolate PBMCs, which are cryopreserved as a cell bank. Clients can bypass the lengthy immunization period and proceed directly to the screening process, significantly saving antibody development time. Through customized screening services, obtain multiple antibody molecules that best suit the application requirements.
Wuhan Nano Body Life Science and Technology Co. Ltd. (NBLST) is a nanobody industry platform established under the initiative of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute. Its headquarters is located in the main building of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute in the East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan. It boasts a 1400 m² independent laboratory in the Precision Medicine Industrial Base of Wuhan Biolake. Additionally, NBLST has established alpaca experimental and transfer bases in Zuoling, Wuhan, and Tuanfeng, Huanggang, both compliant with laboratory animal standards. These bases currently house over 600 alpacas, providing "zero-immunization-background" guaranteed alpaca immunization services for research institutions and antibody drug development companies.
NBLST focuses on the development, engineering, and application of nanobodies, and is dedicated to building an integrated public experimental service platform for production, education, and research. It possesses a full-chain technology platform encompassing antigen preparation (peptides, proteins, and RNA), antibody discovery and engineering, through to biological function validation/screening. The RNA antigens include RNA structurally and sequentially optimized for alpacas. Antibody discovery and engineering services employ multiple technological routes, including phage display, RNA, and mammalian cell display. Through cross-complementation of multiple platforms, it provides flexible antibody discovery and engineering services for pharmaceutical companies and research institutes, facilitating the development of drug reagents.
If you require our services, please feel free to contact us via email: marketingdept@nanobodylife.com