尽管疫苗和抗病毒药物在不断进步,但呼吸道病毒感染的预防和传播在全球范围内仍面临着重大挑战。现有方法的一个明显局限是,它们无法在感染初始部位(呼吸道黏膜)提供强效保护。近日,在 nature nanotechnology上发表的一篇文章《Engineered mucus-tethering bispecific nanobodies enhance mucosal immunity against respiratory...
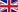
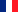
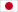
尽管疫苗和抗病毒药物在不断进步,但呼吸道病毒感染的预防和传播在全球范围内仍面临着重大挑战。现有方法的一个明显局限是,它们无法在感染初始部位(呼吸道黏膜)提供强效保护。近日,在 nature nanotechnology上发表的一篇文章《Engineered mucus-tethering bispecific nanobodies enhance mucosal immunity against respiratory pathogens》其研究结果表明,设计策略通过阻断病毒入侵和限制传播链,为增强呼吸道病毒的黏膜防御提供了新思路。本文章研究者设计了一种黏液锚定双特异性纳米抗体。其设计目的是通过结合病毒表面蛋白来中和病毒,同时通过将病毒固定在黏蛋白上,将其捕获在黏液层中。与传统的非黏液锚定纳米抗体相比,这些双特异性纳米抗体在呼吸道中的滞留时间增加,为小鼠提供了更强的抗流感病毒感染保护,并减少了仓鼠模型中的SARS-CoV-2传播。接下来我们就一起来看一下这项研究获得的成果以及它带来的意义。

Currently, for diseases like FEVR, existing methods (laser, surgery) can only address complications (such as bleeding, detachment) but cannot fundamentally correct vascular developmental defects. Therapies targeting the underlying cause are completely lacking. However, in 2024, Boehringer Ingelheim licensed the FZD4 agonist SZN-413 for a potenti...
Currently, for diseases like FEVR, existing methods (laser, surgery) can only address complications (such as bleeding, detachment) but cannot fundamentally correct vascular developmental defects. Therapies targeting the underlying cause are completely lacking. However, in 2024, Boehringer Ingelheim licensed the FZD4 agonist SZN-413 for a potential total of $599 million. This is not just a single project deal but signifies strong recognition by a top pharmaceutical company of the entire target's biology and translational pathway. The development of SZN-413 indicates a new direction in the treatment of ophthalmic diseases.Next, let's get to know the FZD4 (Frizzled-4) target.