In recent years, significant progress has been made in CD7-targeted immunotherapies, particularly in the CAR-T field. Several CD7-targeted CAR-T products have entered clinical research for treating relapsed/refractory T-cell malignancies. For example, UCART7, developed by Servier, is an allogeneic CAR-T product. It involves genetically editing T cells from healthy donors to introduce a CD7-targeting CAR while simultaneously knocking out the T cells' own CD7 and TCR genes to avoid graft-versus-host disease and fratricide. Another product, RD13-01 from Binhui Biotechnology, also employs a gene editing strategy to generate CD7 and TCR double-knockout CAR-T cells. This product has entered clinical research stages, with early data indicating its potential therapeutic efficacy against CD7-positive tumors.
Key Advantages of CD7 in in-vivo CAR Platforms
Utilizing CD7 as a targeting molecule offers several distinct advantages in in vivo CAR generation platforms (such as targeted LNPs, targeted lentiviral vectors, or other delivery vehicles):
-
High Targeting Specificity: Using CD7 to direct vectors to T/NK cells allows for the direct in vivo engineering of these effector cells, avoiding the time-consuming and labor-intensive process of peripheral cell collection and ex vivo expansion.
-
Broad Coverage: CD7 is expressed on various subsets including CD4+, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells. This enables the same targeting strategy to potentially engineer multiple effector cell types simultaneously, broadening the diversity of therapeutic mechanisms.
-
Controllable & Repeatable Dosing: Achieving a "single-dose" effect is feasible. Using transient expression systems (e.g., mRNA) or regulatable vectors can reduce long-term gene insertion risks and make efficacy/toxicity more manageable. Relevant reviews and platform reports indicate that CD7-targeted delivery strategies can effectively achieve intracellular CAR expression and produce functional effects in animals and early-stage studies. Interius BioTherapeutics announced that its in vivo candidate (INT2104, designed to use a CD7-binder to target vectors to CD7⁺ T/NK cells and generate anti-B-cell CARs in vivo) has completed dosing in the first subject and entered clinical evaluation (based on public news releases and company statements). This serves as a direct clinical example of an in vivo approach using CD7 as an "anchor."
Advantages of Nanobodies in CD7 Targeting
Although significant progress has been made in CD7-targeted drugs, traditional antibodies still face numerous challenges. Widespread CD7 expression on normal T cells means systemic targeting can easily lead to immunosuppression and increased infection risk. In CAR-T design, CD7-positive T cells may engage in fratricide, impacting efficacy and in vivo expansion. Furthermore, structural and glycosylation differences of the CD7 protein across different cell subsets pose challenges for antibody recognition specificity. These issues significantly hinder the development of CD7-targeted drugs.
Compared to traditional antibodies, CD7 nanobodies offer significant structural and functional advantages. Beyond their small size and low immunogenicity, their precise targeting capability and ease of engineering provide strong support for therapeutic antibody development. Recently, the CDE (Center for Drug Evaluation) website announced that PA3-17 injection, developed by PersonGen BioTherapeutics, has been proposed for inclusion in the Breakthrough Therapy Designation program. It is intended for treating adult relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoblastic lymphoma. In early clinical trials, PA3-17 demonstrated an objective response rate as high as 84.6%, with 76.9% of patients achieving complete remission, indicating significant anti-tumor efficacy. Unlike traditional allogeneic CAR-T, it is an autologous CAR-T product. It utilizes the patient's own CD7-negative T cells to construct the CAR-T and incorporates the PEBL platform technology to prevent CAR-T cell fratricide. Moreover, the CAR structure in PA3-17 employs a CD7-targeting nanobody as the antigen recognition domain. This design can significantly enhance the stability and target-killing capability of the CAR-T cells.
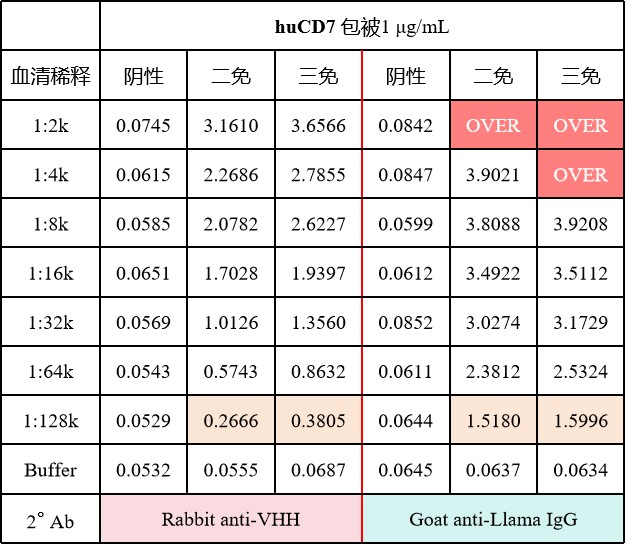
With their unique structural advantages and excellent performance, CD7 nanobodies are bringing new changes to the landscape of precision immunotherapy, offering novel breakthrough opportunities for oncology and other fields. Nabobiosciences offers a CD7 Off-the-Shelf Immune Library (ELISA serum titer data shown in the figure below). After alpaca immunization, we collect whole blood, isolate PBMCs, and cryopreserve them as a cell bank. Clients can bypass the lengthy immunization period and proceed directly to the screening process, significantly reducing antibody development time. Through customized screening services, we help you rapidly obtain high-quality antibody molecules that best meet your application needs.
In addition, Nabobiosciences possesses the pDual phage display technology and NabLib® mammalian cell display technology, enabling efficient and developable screening of CD7 nanobodies. The pDual system seamlessly connects the high-throughput screening of phage display with mammalian cell expression, weeding out poorly expressed and unstable molecules early to enhance developability. The NabLib® platform supports various screening configurations, ensuring that the selected nanobodies perform excellently across diverse scenarios such as detection, imaging, and therapy.
Wuhan Nano Body Life Science and Technology Co. Ltd. (NBLST) is a nanobody industry platform established under the initiative of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute. Its headquarters is located in the main building of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute in the East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan. It boasts a 1400 m² independent laboratory in the Precision Medicine Industrial Base of Wuhan Biolake. Additionally, NBLST has established alpaca experimental and transfer bases in Zuoling, Wuhan, and Tuanfeng, Huanggang, both compliant with laboratory animal standards. These bases currently house over 600 alpacas, providing "zero-immunization-background" guaranteed alpaca immunization services for research institutions and antibody drug development companies.
NBLST focuses on the development, engineering, and application of nanobodies, and is dedicated to building an integrated public experimental service platform for production, education, and research. It possesses a full-chain technology platform encompassing antigen preparation (peptides, proteins, and RNA), antibody discovery and engineering, through to biological function validation/screening. The RNA antigens include RNA structurally and sequentially optimized for alpacas. Antibody discovery and engineering services employ multiple technological routes, including phage display, RNA, and mammalian cell display. Through cross-complementation of multiple platforms, it provides flexible antibody discovery and engineering services for pharmaceutical companies and research institutes, facilitating the development of drug reagents.
If you require our services, please feel free to contact us via email: marketingdept@nanobodylife.com