Role of FZD4 in Disease
Ocular Diseases: In Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy (FEVR), mutations in the FZD4 gene disrupt the Norrin/β-catenin signaling pathway, leading to abnormal retinal vascular development, neovascularization, and potentially severe blindness.
Cardiovascular Diseases: In vascular endothelial cells, FZD4 participates in regulating angiogenesis and vascular homeostasis. FZD4 is upregulated in response to disturbed blood flow, promoting endothelial inflammation and increased permeability, and is involved in the process of atherosclerosis.
Cancer: In tumors such as lung cancer, abnormal FZD4 expression affects tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Targeted delivery against it can inhibit metastasis, suggesting its therapeutic potential.
Currently, R&D targeting FZD4 (e.g., agonist SZN-413) is advancing from preclinical to clinical stages, with particularly urgent demand in the field of inherited retinal diseases. Specific agonists, represented by SZN-413, are the primary direction of exploration.
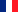
Structure and Function of FZD4
FZD4 (Frizzled-4) is an important transmembrane receptor protein belonging to the Frizzled family. It plays key roles in various physiological and pathological processes. Below is relevant information about the FZD4 target:
Structure of FZD4:
Extracellular N-terminal Domain: This is the signal recognition region, containing a cysteine-rich domain responsible for high-affinity, specific binding to the ligand Norrin (primarily) or Wnt proteins.
Seven-transmembrane Core Domain: This is the hallmark of the G protein-coupled receptor family, responsible for undergoing conformational changes after ligand binding to transmit the signal from outside to inside the cell.
Intracellular C-terminal Tail: This is the signal amplification region, containing a conserved segment responsible for recruiting downstream signaling proteins like Dishevelled to initiate signal cascades.
Basic Function of FZD4:
FZD4 is a crucial receptor in the Wnt signaling pathway, involved in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and tissue development. By binding to Wnt ligands or specific non-Wnt ligands (like Norrin), it activates downstream signaling pathways, influencing cell behavior and gene expression.
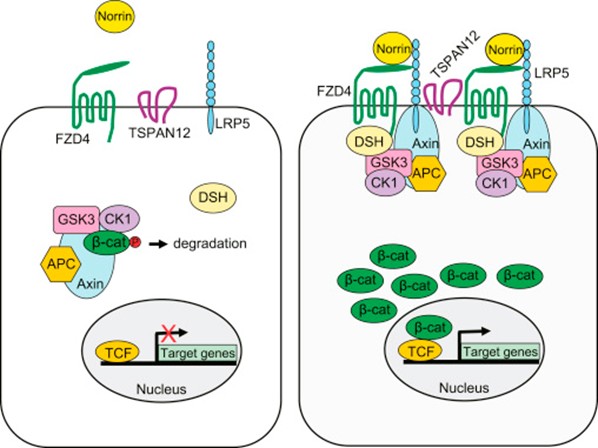
Schematic diagram of the Norrin-β-Catenin signaling pathway
Current Status of FZD4 Drug R&D
Drug R&D related to the FZD4 target is currently at various stages, mainly focused on ophthalmic diseases and cancer treatment. Currently, the development of FZD4-targeted drugs is highly concentrated on ophthalmic diseases, with the primary strategy being to activate the pathway via agonists to promote healthy retinal vascular regeneration.
-
SZN-413:This is currently the most advanced and representative FZD4-targeted therapy. It is a FZD4-specific Wnt signaling pathway agonist. Preclinical studies show it can effectively stimulate normal retinal vascular regeneration and inhibit pathological neovascularization. Development Challenge: FZD4 is part of the Wnt pathway, whose aberrant activation is associated with various cancers. Therefore, the core challenge in drug development is achieving tissue-specific (ocular) precise activation while avoiding systemic off-target effects and carcinogenic risks. The bispecific design and local administration (e.g., intravitreal injection) of SZN-413 are precisely to address this challenge.
-
SZN-8141(Bispecific Antibody):Combines FZD4 agonist and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antagonist properties, aiming to simultaneously modulate the FZD4 signaling pathway and inhibit VEGF activity. Intended for treating diseases like Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) and Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (Wet AMD). Preclinical data show it can reduce vascular leakage and pathological angiogenesis. Currently in the preclinical research stage.
Advantages of Nanobodies in FZD4 Drug R&D
Nanobodies offer the following significant advantages in FZD4-targeted drug R&D: High Tissue Penetration: Their small molecular weight allows them to penetrate tissue spaces more effectively, reaching the FZD4 target. Particularly in tissues like the retina, they can exert their regulatory role better, for example, acting more precisely on lesions when treating retinopathies. High Affinity and Specificity: The long CDR3 region of nanobodies enables recognition of hidden or conformation-dependent epitopes on the FZD4 receptor, providing high binding specificity and affinity for FZD4. This allows for precise regulation of the FZD4-mediated Wnt signaling pathway, reducing off-target effects. Heat Resistance and Stability: They are resistant to high temperatures and stable, facilitating formulation development and long-term storage. This suits scenarios like ophthalmology requiring local drug administration, ensuring the drug remains active in the body. Ease of Engineering: They can be engineered via genetic engineering to create bispecific or multispecific nanobodies, for example, simultaneously targeting FZD4 and other related targets like VEGF to achieve synergistic therapy and improve treatment efficacy for complex diseases. In diseases like Wet AMD, this could allow simultaneous inhibition of pathological angiogenesis and promotion of normal vascular repair. Reports have demonstrated that nanobodies can successfully disrupt LGR4-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling upon Norrin stimulation [1].
Nanobodies in FZD4-targeted drug R&D combine high efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness, offering new technological pathways for treating diseases related to the FZD4 signaling pathway, such as retinopathies and central nervous system diseases.
NBLST possesses the pDual improved dual-function phage display technology within its NabLib® platform. This technology builds upon the efficient development of traditional phage display, seamlessly connecting to small-scale mammalian cell production, greatly improving the efficiency of screening out problematic molecules. Furthermore, the NabLib® mammalian cell display technology not only enhances the developability of screened molecules but also allows flexible selection of antibody screening formats, providing better assurance for downstream antibody molecule application and detection.

Wuhan NanoBody Life Science and Technology Co. Ltd. (NBLST) is a nanobody industry platform established under the initiative of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute. Its headquarters is located in the main building of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute in the East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan. It boasts a 1400 m² independent laboratory in the Precision Medicine Industrial Base of Wuhan Biolake. Additionally, NBLST has established alpaca experimental and transfer bases in Zuoling, Wuhan, and Tuanfeng, Huanggang, both compliant with laboratory animal standards. These bases currently house over 600 alpacas, providing "zero-immunization-background" guaranteed alpaca immunization services for research institutions and antibody drug development companies.
NBLST focuses on the development, engineering, and application of nanobodies, and is dedicated to building an integrated public experimental service platform for production, education, and research. It possesses a full-chain technology platform encompassing antigen preparation (peptides, proteins, and RNA), antibody discovery and engineering, through to biological function validation/screening. The RNA antigens include RNA structurally and sequentially optimized for alpacas. Antibody discovery and engineering services employ multiple technological routes, including phage display, RNA, and mammalian cell display. Through cross-complementation of multiple platforms, it provides flexible antibody discovery and engineering services for pharmaceutical companies and research institutes, facilitating the development of drug reagents.
In addition to its natural nanobody library, NBLST also offers an off-the-shelf immunized library to help clients quickly screen for antibody molecules that meet their needs.
If you require our services, please feel free to contact us via email: marketingdept@nanobodylife.com