Research Cotent
Screening and Construction of Nanobodies
Screening: Using yeast surface display technology, specific nanobodies targeting human MUC5AC mucin, murine Muc5ac mucin, H1N1 influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) protein, and SARS-CoV-2 spike (Spike) protein were rapidly identified from a library of over 5×10⁸ synthetic sequences (binding validation shown in Figure 1h, i).
Construction: Bispecific nanobodies (e.g., Nb.I9-M6, Nb.S13iD-M6) were generated by fusing virus-neutralizing nanobodies (e.g., Nb.I9 targeting H1N1 HA, Nb.S13iD targeting SARS-CoV-2 Spike) with mucus-binding nanobodies (e.g., Nb.H17 targeting human MUC5AC, Nb.M6 targeting murine Muc5ac) via head-to-tail ligation.Affinity maturation of selected SARS-CoV-2 nanobodies was performed using error-prone PCR, and homodimers were constructed to enhance neutralizing potency.
IN Vitro Validation
Mucus Protection Assay: Calu-3 human lung epithelial cells (mucus-secreting) and MDCK cells were treated with StcE enzyme (degrades mucins) and IL-13 (stimulates mucus secretion) to verify the physical barrier function of the mucus layer—particularly MUC5AC—in protecting against H1N1 infection (Figure 1b, d, f, g).
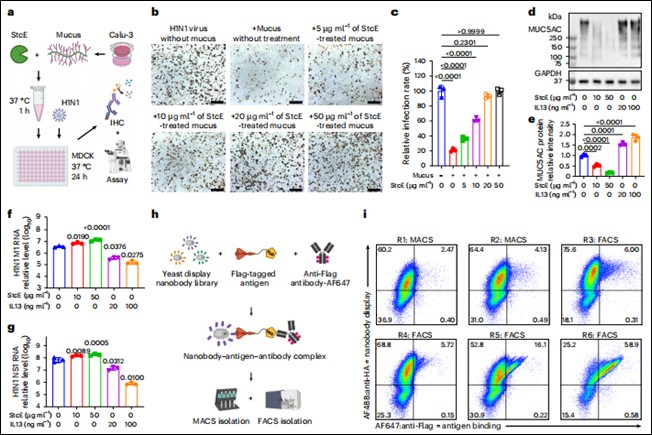 Figure 1. Protective effect of the mucus layer is independent of mucin structure
Figure 1. Protective effect of the mucus layer is independent of mucin structure
Nanpbody Binding and Neutralization Validation: Immunofluorescence and Western blot confirmed nanobody binding to targets (mucus/viral proteins). Live virus neutralization assays (H1N1/MDCK cells) and pseudovirus neutralization assays (SARS-CoV-2/hACE2-293T cells) evaluated neutralizing efficacy (Figure 2d, e, h, i).
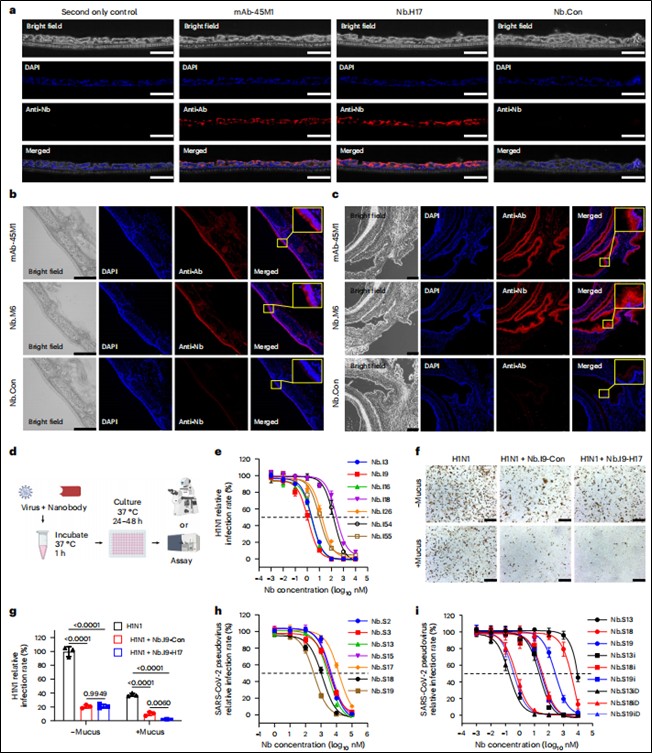 Figure 2. Development and validation of mucus-tethering and virus-neutralizing functions
Figure 2. Development and validation of mucus-tethering and virus-neutralizing functions
IN Vivo Animal Model Experiments
Pharmacokinetic Study: Fluorescently labeled nanobodies were administered intranasally to mice. In vivo/ex vivo optical imaging and immunofluorescence staining compared the retention time of tethered vs. non-tethered nanobodies in the respiratory tract (nasopharynx, lungs).
Prolonged Respiratory Retention via Mucus Tethering: In vivo imaging showed that mucus-tethered bispecific nanobodies (Nb.I9-M6) remained in the murine nasopharynx and lungs for over 72 hours—significantly longer than non-tethered counterparts (Nb.I9-Con). Retention was mediated by binding to the mucosal surface rather than epithelial cell uptake (Figure 3).
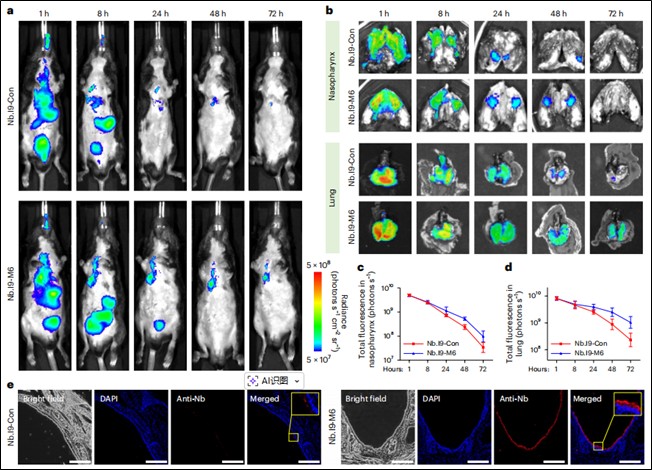 Figure 3. Long-term in vivo retention of mucus-tethered nanobodies
Figure 3. Long-term in vivo retention of mucus-tethered nanobodies
Influenza Prevention and Treatment Models(Mice)
Prevention Model: Nanobodies were administered intranasally at different time points (1h, 24h, 48h) before challenge with low-dose (250 PFU) or high-dose (2500 PFU) H1N1 virus. Body weight changes, survival rates, lung viral loads (qPCR for M1/NS1 genes), and pathological damage were monitored (Figure 4).
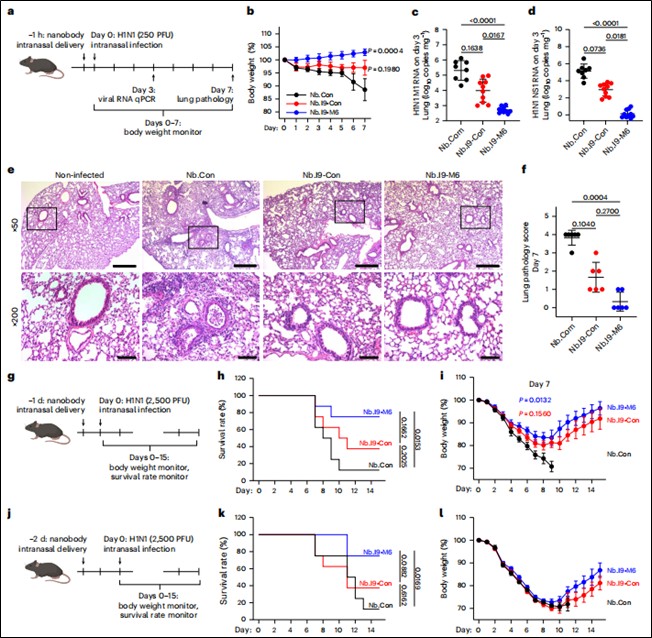 Figure 4. Mucus-tethered bispecific nanobodies prevent H1N1 infection in mice
Figure 4. Mucus-tethered bispecific nanobodies prevent H1N1 infection in mice
Treatment Models: Nanobody administration began intranasally on days 1–2 or 3–7 post-infection to evaluate therapeutic efficacy in already infected animals (Figure 5).
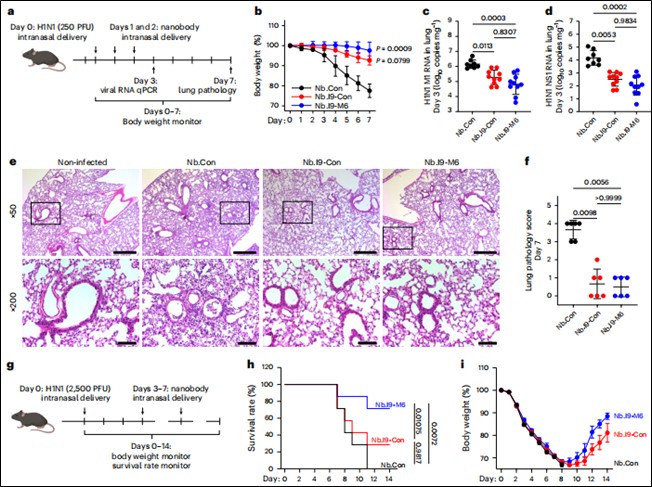 Figure 5. Therapeutic efficacy of mucus-tethered bispecific nanobodies against H1N1 infection
Figure 5. Therapeutic efficacy of mucus-tethered bispecific nanobodies against H1N1 infection
SARS-CoV-2 Transmission Model(Hamsters)
Cohabitation Transmission Model: "Donor" hamsters were first infected, then co-housed with "recipient" hamsters pre-treated with nanobodies for a specified duration. Recipient hamsters were monitored for body weight, viral RNA loads, and infectious viral titers in the upper/lower respiratory tract (oral swabs, nasal turbinates, lungs) to assess transmission-blocking efficacy (Figure 6).
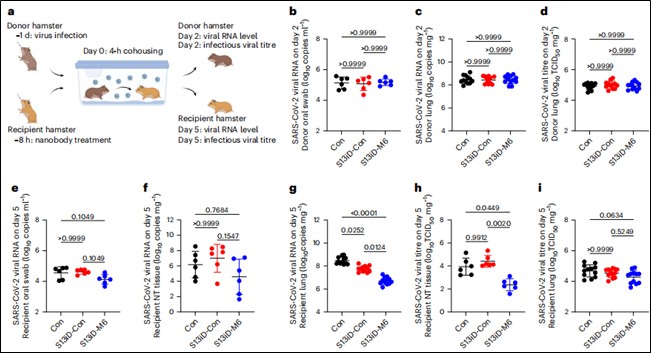
Figure 6. Mucus-tethered bispecific nanobodies reduce SARS-CoV-2 transmission in hamster cohabitation models with 8-hour pre-treatment
Conclusion
This study presents and validates an innovative mucosal immunity enhancement strategy: engineering bispecific nanobodies to target both respiratory viral surface proteins and mucosal mucins (MUC5AC). This "tethering" strategy enables Physically trapping viral particles in the mucus layer, preventing contact with and infection of underlying epithelial cells; Significantly extending the retention time of therapeutic molecules at respiratory infection sites, achieving long-acting protection; Effectively preventing infection, reducing disease severity, and blocking viral transmission in influenza mouse models and SARS-CoV-2 hamster transmission models, demonstrating both preventive and therapeutic potential; Bypassing the long time required to induce active immune responses, providing an "off-the-shelf" mucosal defense approach.
Significance
This research develops a promising, ready-to-use biotherapeutic platform that "intercepts" pathogens by enhancing virus-mucus interactions, offering a new powerful tool for preventing and treating respiratory viral infections. It advances the application of nanobodies in mucosal immunity, highlighting their unique advantages—small size, ease of engineering, and high stability—in mucosal drug delivery and local immunotherapy. The study also identifies future optimization directions: tailoring the affinity of mucus-binding nanobodies for different species or individuals is key to maximizing protective efficacy. Combining this strategy with targeting of conserved viral epitopes could address viral mutations.
Wuhan NanoBody Life Science and Technology Co. Ltd. (NBLST) is a nanobody industry platform established under the initiative of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute. Its headquarters is located in the main building of the Wuhan Industrial Innovation and Development Research Institute in the East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan. It boasts a 1400 m² independent laboratory in the Precision Medicine Industrial Base of Wuhan Biolake. Additionally, NBLST has established alpaca experimental and transfer bases in Zuoling, Wuhan, and Tuanfeng, Huanggang, both compliant with laboratory animal standards. These bases currently house over 600 alpacas, providing "zero-immunization-background" guaranteed alpaca immunization services for research institutions and antibody drug development companies.
NBLST focuses on the development, engineering, and application of nanobodies, and is dedicated to building an integrated public experimental service platform for production, education, and research. It possesses a full-chain technology platform encompassing antigen preparation (peptides, proteins, and RNA), antibody discovery and engineering, through to biological function validation/screening. The RNA antigens include RNA structurally and sequentially optimized for alpacas. Antibody discovery and engineering services employ multiple technological routes, including phage display, RNA, and mammalian cell display. Through cross-complementation of multiple platforms, it provides flexible antibody discovery and engineering services for pharmaceutical companies and research institutes, facilitating the development of drug reagents.
In addition to its natural nanobody library, NBLST also offers an off-the-shelf immunized library to help clients quickly screen for antibody molecules that meet their needs.
If you require our services, please feel free to contact us via email: marketingdept@nanobodylife.com