- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 468
With the groundbreaking progress of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in human cancer therapy, the demand for similar treatments in companion animals, such as dogs, is increasingly growing. Spontaneous canine tumors share high similarities with human tumors in terms of immune microenvironment, genetic background, and clinical progression, making them ideal translational medicine models. However, the market still lacks efficient and specific immunotherapeutic drugs targeting canine PD-L1. Most existing antibodies are derived from murine sources or are humanized, suffering from issues like strong immunogenicity, high production costs, and poor tissue penetration. Therefore, developing a novel canine PD-L1-targeting inhibitor based on Nanobodies (Nbs) holds promise not only for advancing veterinary oncology but also for providing valuable references for human immunotherapy research.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 577
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is primarily categorized into HSV-1 and HSV-2. The former often causes oral herpes, while the latter is a major cause of genital herpes. Both viruses can disseminate to other organs or lead to severe, potentially fatal complications, including herpes keratitis, herpes encephalitis, neonatal herpes, among others. Existing therapeutics like acyclovir can only inhibit viral replication but cannot prevent latent infection or recurrence. Furthermore, as the viral glycoprotein B (gB) undergoes conformational changes, the number of drug-resistant viral strains continues to rise annually.
- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 472
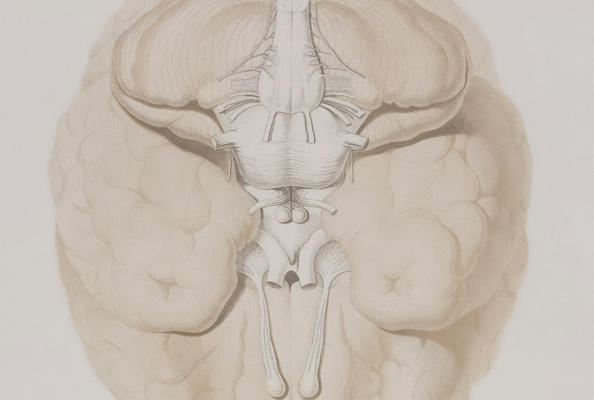
The lack of effective treatments for brain disorders related to NMDA receptor hypofunction, such as schizophrenia and GRIN1-related disorders, has long been a major challenge in the medical field. Traditional small-molecule drugs often lack selectivity and exhibit significant side effects, while antibody-based therapies struggle to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB), limiting their efficacy.To address this clinical need, a collaborative effort involving the Institute of Functional Genomics in Montpellier (France), the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University of Toronto (Canada), and the Faculty of Health, Medicine, and Technology at Paris-Saclay University (France) has developed a bivalent bispecific nanobody named DN13-DN1. Administered via intraperitoneal (IP) injection, this nanobody successfully crosses the BBB, specifically binds to and enhances the activity of the mGlu2 receptor. In two mouse models of NMDA receptor hypofunction—neonatal PCP-induced (mimicking schizophrenia) and GluN1-KD genetic (mimicking GRIN1 disorder)—DN13-DN1 significantly improved cognitive deficits and sensorimotor gating impairments. Subchronic treatment demonstrated stable therapeutic effects without noticeable side effects, outperforming both traditional small-molecule drugs and IgG-class antibodies. This study was published in the leading academic journal Nature. Let’s delve into the details.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 421
In modern medical diagnostics and life science research, proteins serve as key biomarkers directly linked to disease phenotypes, making their accurate and rapid detection highly important. However, conventional detection technologies face multiple limitations. For example, immunoassays such as ELISA require tedious separation and washing steps or depend on stringent conditions for antibody pairs, making it difficult to meet the needs of point-of-care testing and high-throughput analysis. Although mass spectrometry is considered the "gold standard" in proteomics research, it relies on large, expensive equipment and involves lengthy analytical procedures.