- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 294
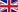
In the long-standing battle between humans and viruses, the continuous mutation of viruses resembles an arms race where “as virtue rises one foot, vice rises ten.” As the shadow of the COVID-19 pandemic gradually recedes, we are still not entirely free from the threat posed by coronaviruses. The emergence of new viral variants continues to challenge global public health security. Against this backdrop, a research team comprising multiple world-renowned institutions, including the University of Pittsburgh, has successfully screened a type of pan-sarbecovirus nanobody (psNbs) with "super immunity" from immunized alpacas using innovative technological approaches. This study, published in Cell Reports, aims to identify a universal solution capable of combating an entire virus family.
- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 350
In plant biology research, deciphering protein localization, interactions, and dynamics is central to unraveling life's mechanisms. Traditional protein tagging techniques relying on fluorescent proteins or epitope tags are often hindered by large tag size, insufficient affinity, or limited applicability. This is particularly problematic for "hard-to-tag" proteins such as multi-pass transmembrane proteins (e.g., metal transporters) and functionally sensitive proteins, where traditional methods can disrupt their structure and function, bringing research to a halt. Nanobodies, with their advantages of high affinity and genetic encodability, offer a potential solution to this bottleneck. While the ALFA tag and ALFA nanobody system have previously demonstrated excellent performance in animal and yeast cells, their applicability in plants had not been systematically evaluated.

- Details
- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 235
Headache is one of the most common neurological disorders worldwide. Data indicates that approximately 52% of the global population has experienced the affliction of headaches, making it one of the leading causes of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).

- Details
- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 216
In modern society, the demands on individuals are far higher than those in the past few decades. Faced with high-pressure, high-intensity, and highly competitive learning and working environments, as well as complex and ever-changing family and interpersonal relationships, physical and mental exhaustion has become the norm for most people. Moreover, with the development and rise of social networks, ordinary people rely excessively on electronic devices, indulging in the virtual world, short videos, and games—resulting in a severe lack of effective social interaction in real life. Coupled with the pursuit of material possessions in real life, this leads to an imbalance in physical and mental states. Long-term exposure to such an environment has made the incidence of anxiety disorders and depression much higher than in the past.
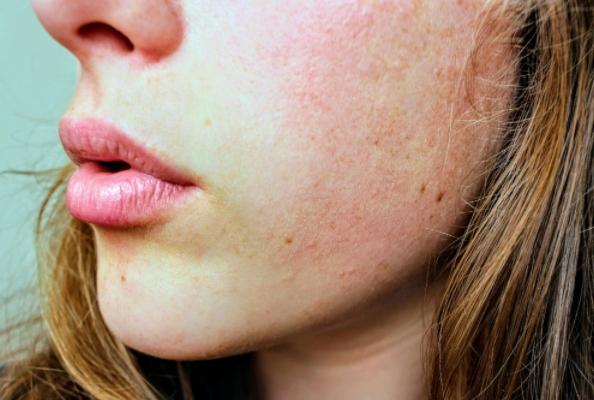

- Details
- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 246
Eczema is a localized inflammatory skin disease, which can be classified into acute eczema, subacute eczema, and chronic eczema based on the disease course. The prevalence rate of eczema in the general population in China is approximately 3%–5%, and that in children is about 10%–20%, making it a relatively common skin disease. Due to the pruritus, erosion, exudation, ulceration, and recurrent attacks of the affected area, eczema seriously affects patients' daily lives.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 280
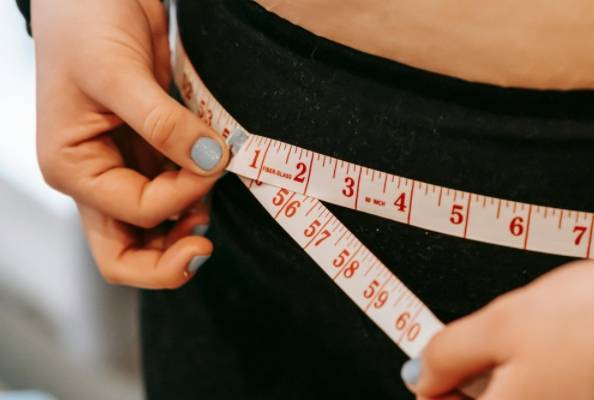
The Dietary Guidelines for Adult Obesity (2024 Edition) released by the National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China indicates that the overweight rate and obesity rate among Chinese citizens aged 18 and above reach 34.3% and 16.4%, respectively. Data from the World Obesity Atlas published by the World Obesity Federation shows that the increase rates of adult obesity and childhood obesity in China are 2.8% and 2%, respectively. Based on the current development trend, it is estimated that by 2030, the number of overweight and obese people in China will account for approximately half of the total population.

- Details
- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 260
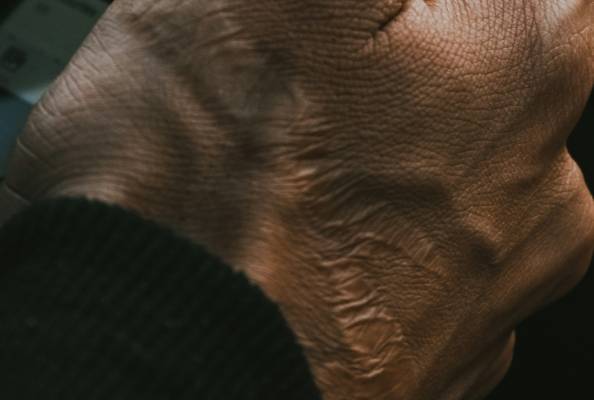
The main pathological feature of tissue fibrosis is the excessive proliferation of fibrous connective tissue in organ tissues, accompanied by a reduction in parenchymal cells, resulting in tissue lesions. If this condition progresses continuously without intervention, it can lead to structural damage and functional decline of organs, and in severe cases, even death [1].
- Details
- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 293
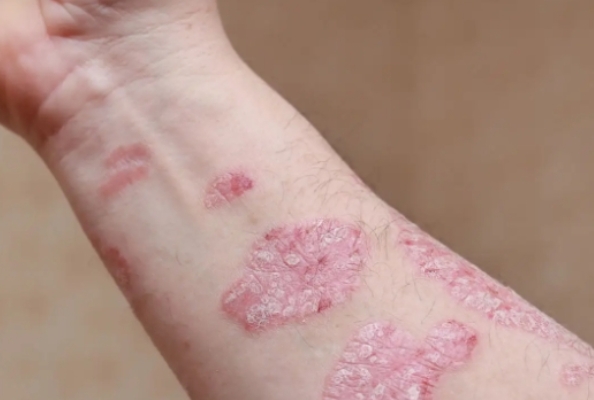
Modern medicine holds that psoriasis is a chronic skin disease caused by multiple factors such as genetic and environmental factors. Similar to lupus erythematosus mentioned earlier in some aspects, it involves immune - mediated factors, which play a crucial role in the occurrence and development of psoriasis.