- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 174
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is an important immunosuppressive receptor expressed mainly on T cells, B cells, natural killer cells, and other immune cells. PD-1 exerts its inhibitory function by binding to its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. In normal immune responses, the activation of PD-1 serves as a self-protective mechanism to prevent an overactive immune system, helping to avoid attacks on self-tissues. However, during tumor immune escape, tumor cells upregulate PD-L1 expression to bind with PD-1, inhibiting T cell activity and thereby evading immune surveillance. Furthermore, abnormal activation of PD-1 also plays a significant role in autoimmune diseases. Through the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands, immune cell activity is suppressed, preventing the immune system from effectively clearing abnormal self-cells or tissues, which is an important mechanism in the development of various autoimmune diseases.
- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 172
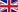
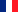
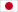
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are one of the most important signal transduction protein families in human cell membranes, regulating a wide range of physiological processes from vision and olfaction to cardiovascular function. Among them, the Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor (AT1R) plays a central role in blood pressure regulation, fluid balance, and cardiovascular diseases. However, the activation mechanism of peptide ligand-binding GPCRs like AT1R has long been a research bottleneck, as traditional methods struggled to capture their active conformations, hindering the precise development of targeted therapeutics. A research team from Harvard Medical School, Duke University, and other institutions has successfully overcome this challenge using synthetic nanobody technology. Their findings, published in Cell, pave a new path for GPCR research and drug development.
- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 210
CD7 is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on the surface of T cells, NK cells, and their precursor cells. It is highly expressed, especially in hematological tumors such as T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and lymphoma. As a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, CD7 is involved in T cell activation, adhesion, and signal transduction, playing an important role in lymphocyte development and immune response. It is a significant marker for T-cell malignancies. Due to its specific expression and persistence in pathological states, CD7 has become an ideal target for developing novel immunotherapeutic strategies.
- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 327
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is a highly promising oncolytic virus capable of preferentially replicating in and lysing tumor cells with defective interferon signaling pathways. Its glycoprotein (VSV-G) is the most commonly used envelope glycoprotein for pseudotyping lentiviral vectors and is widely utilized in gene therapy research. However, the natural receptors of VSV-G (the LDL-R family) are expressed on the surface of nearly all cell types, leading to a lack of targeting specificity for both VSV and pseudotyped lentiviruses. This not only results in the infection of normal cells, causing off-target toxicity, but also reduces the efficacy of precise in vivo treatments. It is known that mutations at the K47 and R354 residues of VSV-G can completely abolish its binding to LDL-R while preserving its fusion activity, offering a potential strategy for engineering targeted VSV-G.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 252
CD8 is a membrane-bound glycoprotein widely expressed on cytotoxic T cells (CD8⁺ T cells), certain subsets of natural killer (NK) cells, and specific populations during thymocyte development. It typically exists as a heterodimer of an alpha and a beta chain, functioning as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). It binds to Major Histocompatibility Complex class I (MHC-I) molecules, enhancing the affinity of the TCR for the peptide-MHC complex, thereby promoting downstream signal transduction and T cell activation. CD8 plays a critical role in immune responses and is one of the key effector molecules for the body to clear virus-infected cells and tumor cells. Due to its central role in immune regulation, CD8 has become an important target in tumor immunotherapy, immune cell research, and the exploration of immune regulatory mechanisms.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 275
Data from the National Health Commission of China in 2024 shows that the overweight and obesity rates among Chinese adults have reached 34.3% and 16.4%, respectively, meaning more than half of the adult population is overweight. Obesity is a significant risk factor for diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, various cancers, and metabolic syndrome. It is projected that by 2050, over half of the global adult population will be overweight or obese. Faced with the limited effectiveness of current lifestyle interventions and the side effects of existing medications, the development of novel, safe, and effective anti-obesity strategies is urgently needed.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 292
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting multiple tissues, including the skin, joints, and entheses, severely restricting patients' mobility and diminishing their quality of life and work productivity. Conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) show limited efficacy in some patients. Existing traditional monoclonal antibody (mAb) biologics face challenges due to their large molecular size (approximately 150 kDa) and poor tissue penetration, hindering effective distribution to poorly vascularized tissues like the synovium and entheses. This results in significantly lower drug concentrations in synovial fluid compared to plasma, limiting their therapeutic potential. Studies indicate that only about one-third of patients achieve minimal disease activity (MDA) within six months of initiating biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs. Furthermore, PsA pathogenesis is closely linked to the interleukin-17 (IL-17) cytokine family. Both IL-17A and IL-17F are overexpressed in lesional tissues and form homodimers and heterodimers that collectively drive inflammation. Inhibiting only a single cytokine is often insufficient for optimal therapeutic outcomes. Therefore, developing novel antibody therapies that combine dual-target inhibition with enhanced tissue penetration is crucial for overcoming current treatment bottlenecks in PsA.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 241
T-cell malignancies are a group of highly aggressive hematologic tumors with high relapse rates and generally poor patient prognosis. A significant challenge arises because CD5, a characteristic marker of malignant T-cells, is also expressed on almost all normal T-cells. This makes CD5-targeting CAR-T therapies unable to distinguish friend from foe, leading them to attack normal T-cells and potentially cause immune function failure. Natural Killer (NK) cells, as key effector cells of the immune system, can recognize and eliminate tumor cells without prior antigen sensitization. Furthermore, their surface lacks CD5 expression, making them ideal effector cells for targeting CD5+ tumor cells.