- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 352
Data from the National Health Commission of China in 2024 shows that the overweight and obesity rates among Chinese adults have reached 34.3% and 16.4%, respectively, meaning more than half of the adult population is overweight. Obesity is a significant risk factor for diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, various cancers, and metabolic syndrome. It is projected that by 2050, over half of the global adult population will be overweight or obese. Faced with the limited effectiveness of current lifestyle interventions and the side effects of existing medications, the development of novel, safe, and effective anti-obesity strategies is urgently needed.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 435
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting multiple tissues, including the skin, joints, and entheses, severely restricting patients' mobility and diminishing their quality of life and work productivity. Conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) show limited efficacy in some patients. Existing traditional monoclonal antibody (mAb) biologics face challenges due to their large molecular size (approximately 150 kDa) and poor tissue penetration, hindering effective distribution to poorly vascularized tissues like the synovium and entheses. This results in significantly lower drug concentrations in synovial fluid compared to plasma, limiting their therapeutic potential. Studies indicate that only about one-third of patients achieve minimal disease activity (MDA) within six months of initiating biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs. Furthermore, PsA pathogenesis is closely linked to the interleukin-17 (IL-17) cytokine family. Both IL-17A and IL-17F are overexpressed in lesional tissues and form homodimers and heterodimers that collectively drive inflammation. Inhibiting only a single cytokine is often insufficient for optimal therapeutic outcomes. Therefore, developing novel antibody therapies that combine dual-target inhibition with enhanced tissue penetration is crucial for overcoming current treatment bottlenecks in PsA.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 327
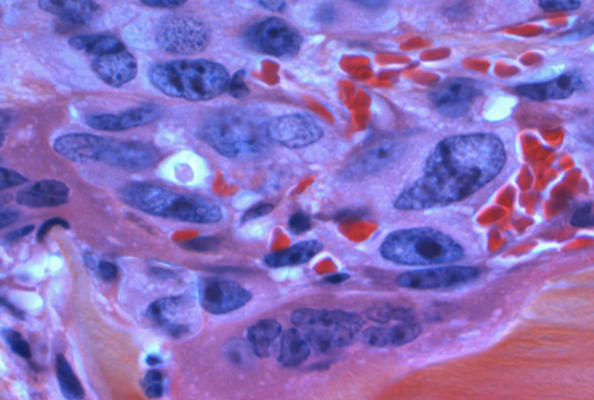
T-cell malignancies are a group of highly aggressive hematologic tumors with high relapse rates and generally poor patient prognosis. A significant challenge arises because CD5, a characteristic marker of malignant T-cells, is also expressed on almost all normal T-cells. This makes CD5-targeting CAR-T therapies unable to distinguish friend from foe, leading them to attack normal T-cells and potentially cause immune function failure. Natural Killer (NK) cells, as key effector cells of the immune system, can recognize and eliminate tumor cells without prior antigen sensitization. Furthermore, their surface lacks CD5 expression, making them ideal effector cells for targeting CD5+ tumor cells.
- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 340
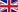
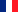
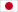
The tumor suppressor protein p16INK4a (p16) plays a critical role in cell cycle regulation by inhibiting CDK4/6 kinase activity, thereby preventing abnormal cell proliferation and acting as a natural "cancer guardian." However, in many cancers, the p16 gene is frequently inactivated by mutations. Missense mutations, in particular, lead to protein structural instability, making p16 prone to degradation or misfolding, and consequently, loss of its tumor-suppressive function. It is estimated that over half of familial melanomas and many sporadic tumors harbor p16 mutations. Traditional gene therapies or small-molecule drugs struggle to directly "fix" such structurally unstable proteins. Therefore, finding molecular chaperones that can stabilize mutant p16 has emerged as a new therapeutic direction.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 478
With the groundbreaking progress of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in human cancer therapy, the demand for similar treatments in companion animals, such as dogs, is increasingly growing. Spontaneous canine tumors share high similarities with human tumors in terms of immune microenvironment, genetic background, and clinical progression, making them ideal translational medicine models. However, the market still lacks efficient and specific immunotherapeutic drugs targeting canine PD-L1. Most existing antibodies are derived from murine sources or are humanized, suffering from issues like strong immunogenicity, high production costs, and poor tissue penetration. Therefore, developing a novel canine PD-L1-targeting inhibitor based on Nanobodies (Nbs) holds promise not only for advancing veterinary oncology but also for providing valuable references for human immunotherapy research.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 590
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is primarily categorized into HSV-1 and HSV-2. The former often causes oral herpes, while the latter is a major cause of genital herpes. Both viruses can disseminate to other organs or lead to severe, potentially fatal complications, including herpes keratitis, herpes encephalitis, neonatal herpes, among others. Existing therapeutics like acyclovir can only inhibit viral replication but cannot prevent latent infection or recurrence. Furthermore, as the viral glycoprotein B (gB) undergoes conformational changes, the number of drug-resistant viral strains continues to rise annually.
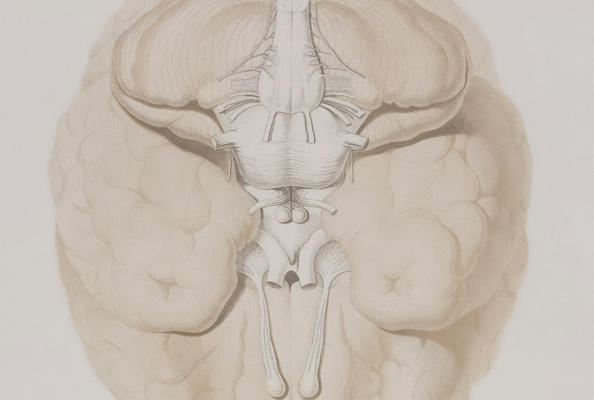
- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 486
The lack of effective treatments for brain disorders related to NMDA receptor hypofunction, such as schizophrenia and GRIN1-related disorders, has long been a major challenge in the medical field. Traditional small-molecule drugs often lack selectivity and exhibit significant side effects, while antibody-based therapies struggle to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB), limiting their efficacy.To address this clinical need, a collaborative effort involving the Institute of Functional Genomics in Montpellier (France), the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University of Toronto (Canada), and the Faculty of Health, Medicine, and Technology at Paris-Saclay University (France) has developed a bivalent bispecific nanobody named DN13-DN1. Administered via intraperitoneal (IP) injection, this nanobody successfully crosses the BBB, specifically binds to and enhances the activity of the mGlu2 receptor. In two mouse models of NMDA receptor hypofunction—neonatal PCP-induced (mimicking schizophrenia) and GluN1-KD genetic (mimicking GRIN1 disorder)—DN13-DN1 significantly improved cognitive deficits and sensorimotor gating impairments. Subchronic treatment demonstrated stable therapeutic effects without noticeable side effects, outperforming both traditional small-molecule drugs and IgG-class antibodies. This study was published in the leading academic journal Nature. Let’s delve into the details.

- Details
-
Also available in:

- Parent Category: Knowledge Base
- Hits: 434
In modern medical diagnostics and life science research, proteins serve as key biomarkers directly linked to disease phenotypes, making their accurate and rapid detection highly important. However, conventional detection technologies face multiple limitations. For example, immunoassays such as ELISA require tedious separation and washing steps or depend on stringent conditions for antibody pairs, making it difficult to meet the needs of point-of-care testing and high-throughput analysis. Although mass spectrometry is considered the "gold standard" in proteomics research, it relies on large, expensive equipment and involves lengthy analytical procedures.